
In 2020 a pandemic swept the world and as of today the global fight against the epidemic remains dire. While masks and safe distances are being promoted, the perception of life is gradually changing and with it a popular technology - ultraviolet (UV) technology.
What is ultraviolet (UV) technology
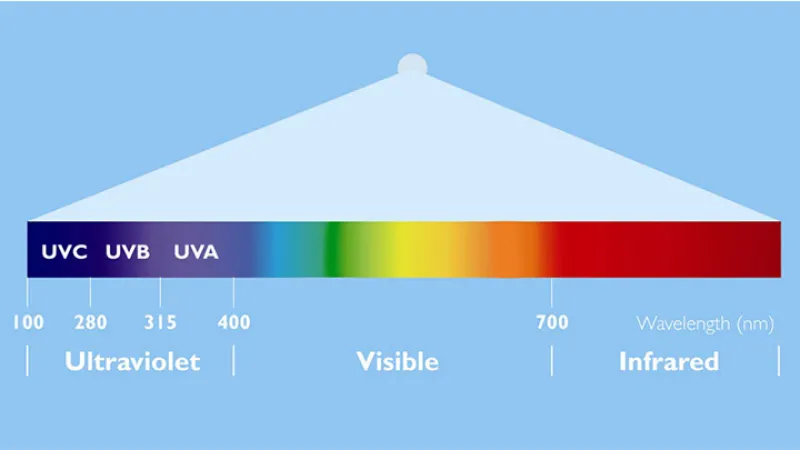
Ultraviolet (UV) light is invisible to the naked eye and is a section of electromagnetic radiation other than visible violet light, in the range of 10 to 400nm, and is divided into three main components - UV-A, UV-B and UV-C.
An ultraviolet ray
UV-A (UV-A, wavelength range 320-420nm) has a strong penetrating power and can reach the dermis of the skin, causing the most damage to the skin, as more than 95% of the daily skin contact is UV-A. At the same time, it activates tyrosinase, leading to immediate melanin deposition and new melanin formation, making the skin darker and less lustrous. 360nm UV-A coincides with the phototropism of insects and can be used as a response curve. response curve and can be used to make insect trap lamps. UVA UV at 300-400 nm can be passed through special tinted glass tubes that completely cut off visible light, radiating only near-ultraviolet light centred at 365 nm. It can be used for ore identification, stage decoration and banknote inspection.
B ultraviolet ray
UV-B ultraviolet ray (UV-B, wavelength range 280-320nm) radiation has medium penetrating power. Most of the medium-wave ultraviolet radiation in daylight will be absorbed by the ozone layer, and only a small part can reach the earth's surface. UVB ultraviolet radiation has an erythematous effect on the human body, can promote the metabolism of minerals in the body and the formation of vitamin D, but long-term or excessive exposure will make the skin tanned. The skin will become red and painful as the nucleic acids and proteins in the epidermal cells are denatured, resulting in symptoms such as acute dermatitis (i.e., sunburn). In severe cases, it can also lead to skin cancer. In addition, long-term damage from UV-B can cause mutations in melanocytes, resulting in sunspots that are difficult to eliminate.
UV-B is often used in plant growth lamps and UV-LED health lamps.

C Ultraviolet rays
C Ultraviolet rays (UV-C, wavelength range 100-280 nm) radiation is a recognized method of disinfection and has been used extensively for over 40 years. It is applied to air, water, and surfaces and can help reduce the risk of infection. UV-C disinfection is effective against all bacteria and viruses tested to date (hundreds have been tested over the years, including various coronaviruses). This clearly shows that UV-C can play an important role in your protection strategy.
Key points to note.
UV-C products need to be used by professionals who know how to use them so that their risks can be minimized. Users must cover their eyes and skin to avoid impaired light exposure and serious damage to the eyes and skin.
